Payment Fraud Trends (2024 – 2025 Update)
19 November 2025Executive Summary
This update on last year’s report analyses global payment fraud trends (Oct 2024–Oct 2025) again draws on Google Trends data and supporting regulatory and enforcement sources to track shifts in public awareness, emerging fraud risks, and regional differences compared with last year.
Here, we identify how fraud awareness and activity have evolved, highlight emerging risks such as AI-enabled scams, and assess the impact of new regulations on global interest and behaviour.
KEY FINDINGS
- Awareness remained steady until mid-2025, then spiked sharply in August–September, coinciding with major UK regulatory reforms.
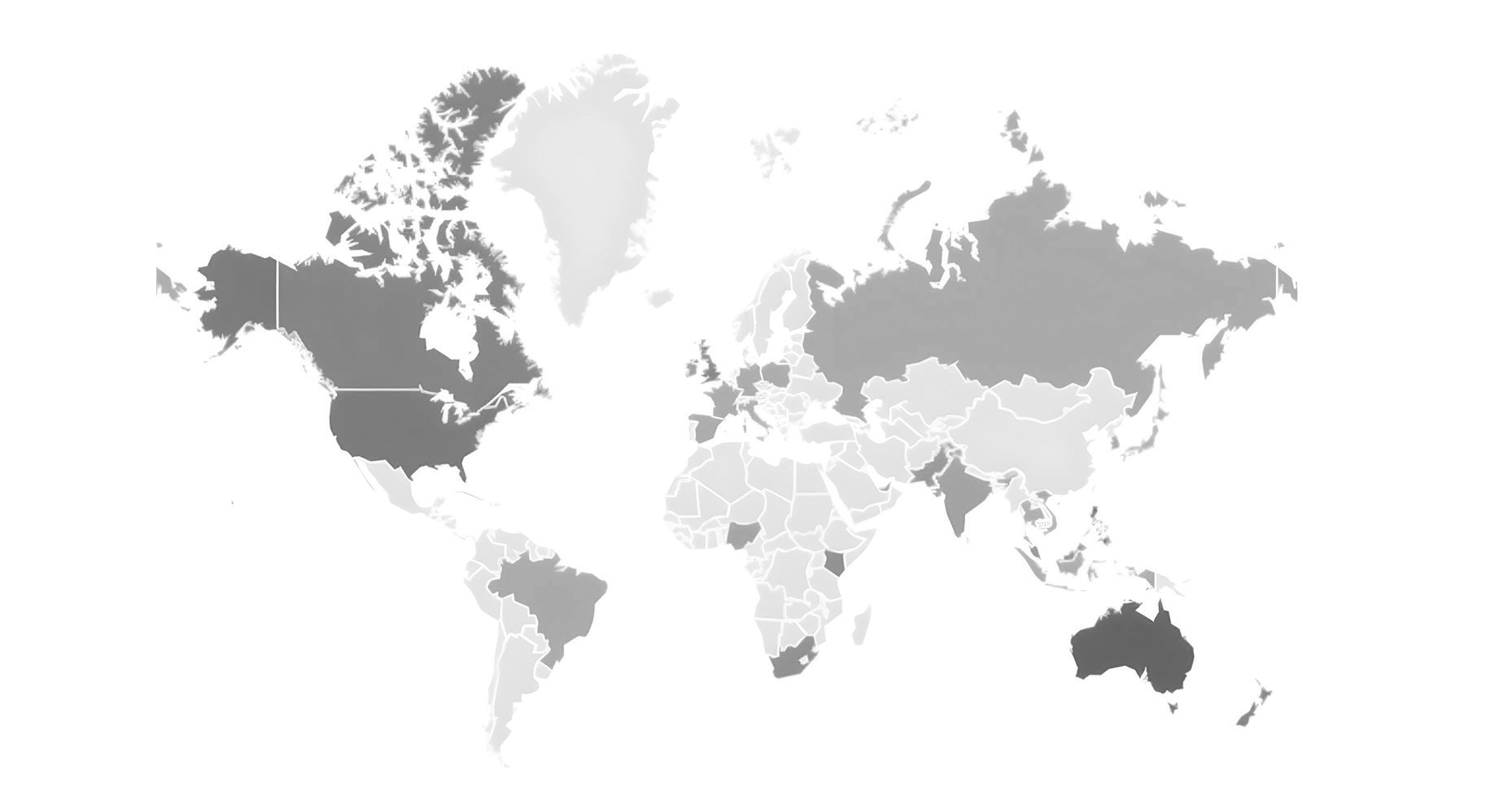
- High engagement in English-speaking and digitally mature markets, notably the UK, US, South Africa, Singapore, and Ireland, reflects strong media and regulatory focus.
- Emerging economies such as India and Kenya show growing search interest as digital payment systems expand.
- AI-assisted and synthetic identity fraud are the most rapidly evolving threats, enabling more scalable and convincing scams.
- Global law-enforcement collaboration intensified, with large operations disrupting cross-border networks and recovering hundreds of millions of dollars.
Global concern about payment fraud is reactive and event-driven, rising around new laws and high-profile incidents but fading quickly. Building sustained public awareness and proactive prevention measures will be essential to staying ahead of increasingly sophisticated fraud tactics.
Introducrions
Digital payments continue to grow worldwide, expanding convenience but also exposure to fraud. Payment fraud remains one of the most reported cybercrimes, and new technologies - especially AI and synthetic identities - are making scams faster and harder to detect.
This 2024–2025 update builds on last year’s report, which looked at long-term (2004–2024) Google trend analysis, to show how global awareness and risk patterns around payment fraud have changed over the past year.
It provides business leaders with a snapshot of:
- Where fraud awareness is rising or lagging;
- How regulation and enforcement drive public attention;
- The emerging fraud types shaping the next wave of risk.
Understanding where awareness is shifting helps businesses anticipate fraud exposure, align compliance efforts, and target prevention resources more effectively. In short: this report translates global search and policy signals into actionable insight for managing financial crime risk.
METHODOLOGY
Findings are based on Google Trends data, analysing global search interest in key terms such as “payment fraud,” “phishing scams,” and “crypto scams.” This approach captures how concern and awareness evolve in near real time, supplemented by secondary research on regulatory events, enforcement actions, and industry reporting.
Part One: Key Global Trends
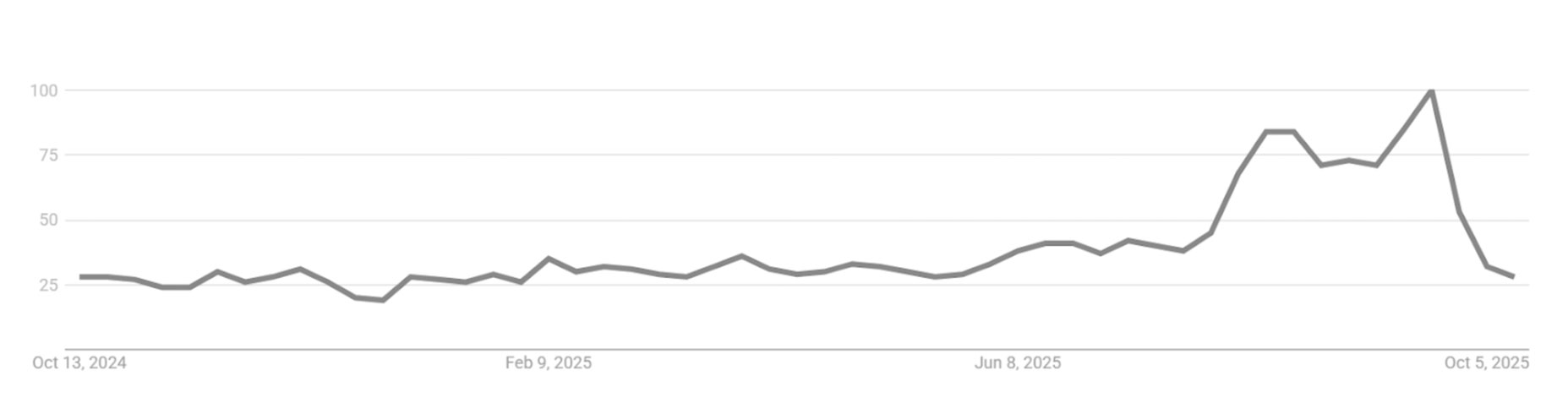
Between late 2024 and mid-2025, global search interest in payment fraud remained steady and moderate, suggesting a consistent baseline of public awareness without major global triggers.
But a clear spike occurred from July to September 2025, reaching its peak in late September before falling sharply in early October. This pattern indicates a largely event-driven awareness cycle, where attention surges in response to external developments and quickly subsides once media coverage fades.
POSSIBLE DRIVERS OF THE 2025 SPIKE
The late-summer surge likely reflects a combination of high-profile events, including:
- Major data breaches or fraud scandals involving banks or payment providers;
- New regulatory or law-enforcement actions, such as the UK’s corporate fraud offence or reimbursement rules;
- Increased media coverage of scams during the lead-up to the global shopping season.
The rapid decline after September shows how quickly fraud awareness returns to baseline once the immediate news cycle passes, highlighting the need for ongoing public education and sustained prevention messaging, rather than reliance on reactive attention spikes.
GLOBAL CONTEXT
The 2024–2025 data shows that public attention to payment fraud followed a consistent baseline pattern punctuated by sharp, event-driven spikes, behaviour typical of financial crime topics on Google Trends.
Analysis of search data and related events suggests several key dynamics:
- Regulation, not incidents, was the dominant awareness trigger. Search peaks closely align with major UK regulatory announcements, particularly the Authorised Push Payment (APP) Reimbursement Rule (October 2024) and the “Failure to Prevent Fraud” corporate offence (September 2025). This indicates that new compliance obligations and enforcement activity drive global attention more than fraud incidents themselves.
- AI-enabled scams gained visibility as an emerging risk theme. Search co-movements between “payment fraud,” “AI scams,” and “deepfake fraud” suggest growing public concern about the role of artificial intelligence in enabling more realistic impersonation and identity manipulation.
- Media amplification reinforced short-term spikes. Coverage of major data breaches and cyberattacks in mid-2025 coincided with the global surge, particularly in English-speaking markets, where reporting on AI-related scams was most prominent.
- Steady baseline interest reflects constant background concern. Despite the volatility of event-driven peaks, baseline search levels remained higher than pre-2023 averages, implying that awareness of digital payment risks is becoming structurally embedded in public discourse.
The global trend indicates a maturing awareness landscape, where regulation and technology shifts now drive as much attention as criminal incidents. However, the brevity of public focus around each spike underscores a critical gap between awareness and sustained vigilance, suggesting an ongoing need for continuous communication, employee training, and consumer education on evolving fraud tactics.
In the next section we will look at regional variations in search interest, revealing which markets show the highest engagement, emerging awareness gaps, and potential hotspots for targeted prevention and risk management efforts.
Part Two: Regional Insights
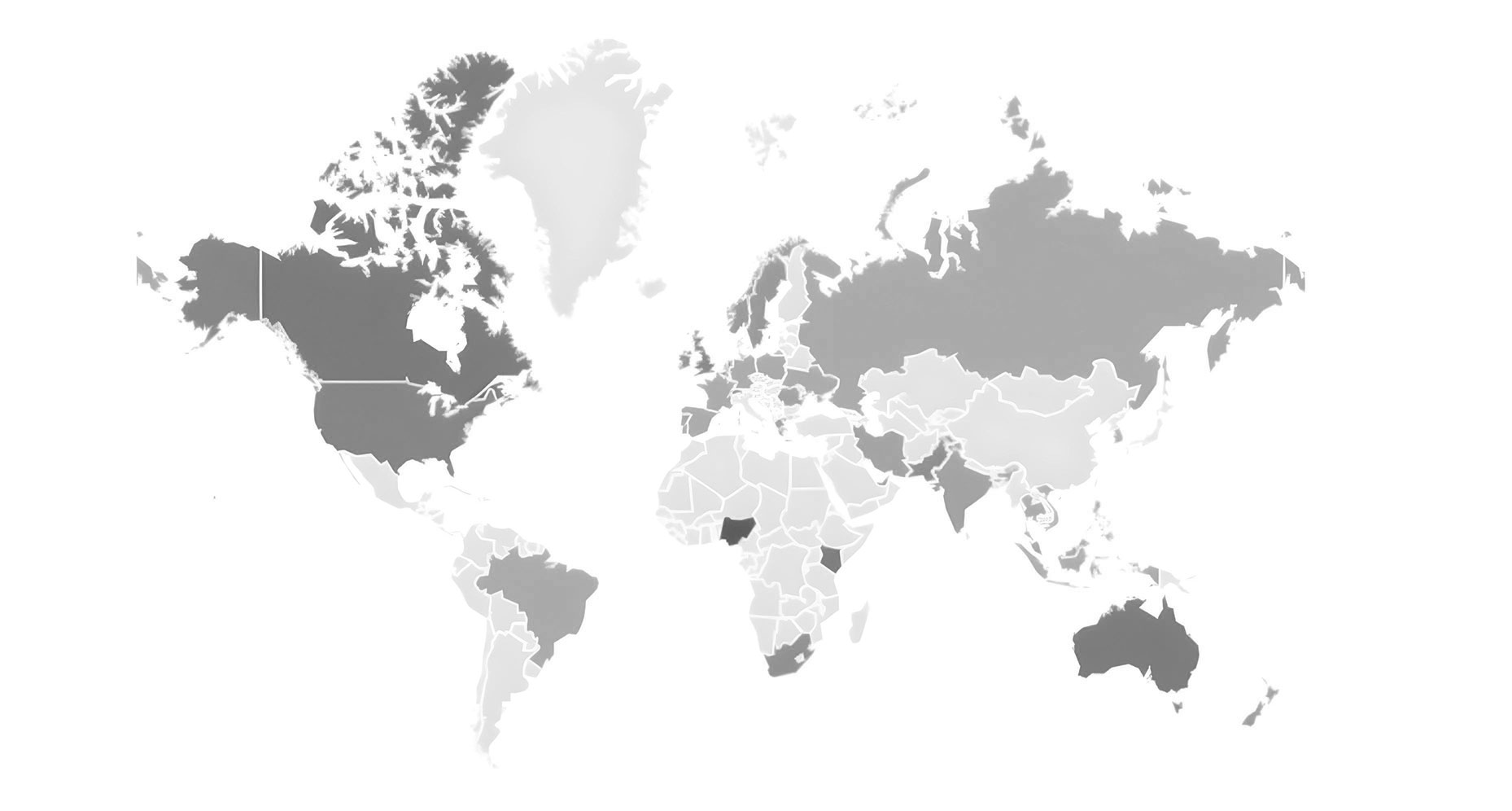
Regional variations in search interest reveal how awareness of payment fraud differs across countries, highlighting emerging hotspots, market-specific risks, and opportunities for targeted prevention efforts.
TOP 10 COUNTRIES BY SEARCH INTEREST (OCT 2024 – OCT 2025)
| Rank | Country | Search Index | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | St. Helena | 100 | Statistical outlier due to small population. |
2 | United Kingdom | 65 | Driven by regulatory activity and media coverage. |
3 | United States | 62 | Consistent high interest; major data breach reporting. |
4 | South Africa | 51 | High digital banking adoption; strong regional concern. |
5 | Singapore | 48 | Fintech hub with proactive fraud awareness. |
6 | Ireland | 44 | Reflects EU regulatory and media focus. |
7 | India | 37 | Rising awareness alongside expanding digital payments. |
8 | Australia | 27 | Moderate engagement; event-driven spikes visible. |
9 | Philippines | 27 | Growing mobile payment adoption; targeted by scams. |
10 | United Arab Emirates | 27 | Rapid digital payments growth; moderate interest. |
These top 10 countries demonstrate that fraud awareness is concentrated in English-speaking and digitally mature markets, where payment penetration is high and regulatory oversight is strong.
The UK and US dominate due to frequent news coverage, regulatory developments, and major corporate fraud prevention campaigns. Emerging markets like India and the Philippines show rising interest, reflecting both growing digital payments adoption and increasing exposure to online scams.
Singapore, South Africa, and Ireland indicate regional hubs where proactive consumer education and regulatory enforcement have heightened public engagement.
High search interest correlates strongly with regulatory visibility, media coverage, and digital payment adoption, rather than absolute fraud volumes. These top-performing countries represent key markets for monitoring trends and targeting prevention efforts, as well as testing new awareness campaigns before broader rollout.
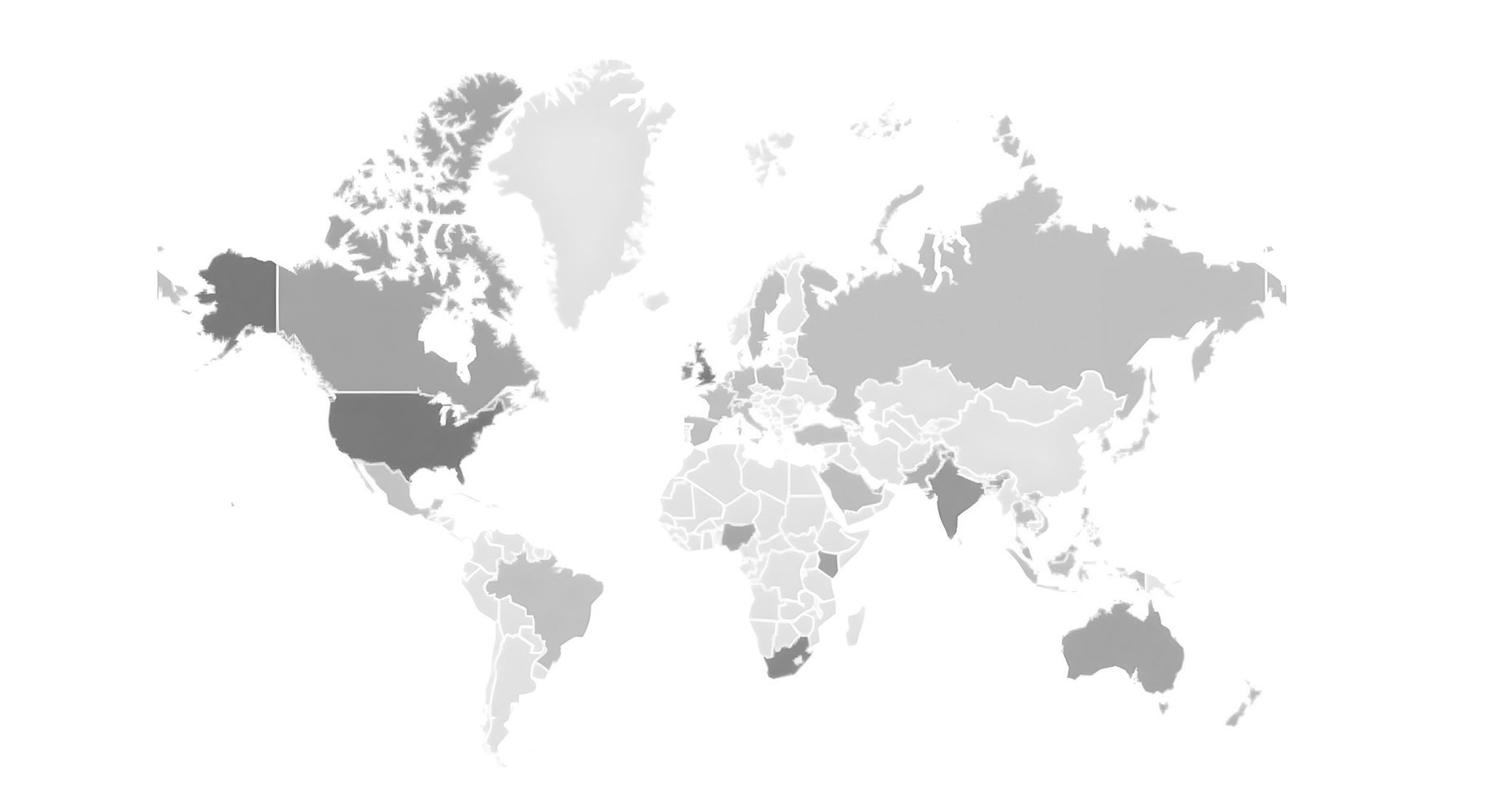
OUTSIDE THE TOP TEN
Mid-Range Interest (10–24 index):
Countries such as Hong Kong, Nigeria, Malaysia, Pakistan, and New Zealand fall in this range. These markets are typically:
- Experiencing rapid adoption of digital and mobile payments;
- Increasingly targeted by cross-border fraud;
- Seeing growing regulatory or consumer-education efforts.
Low-Interest Countries (≤10 index):
Much of continental Europe (e.g., France, Spain, Italy, Germany, Netherlands) and parts of Asia (Vietnam, Thailand, Indonesia) report low search activity. Low search volume does not necessarily indicate low fraud risk; it may reflect:
- Limited public awareness or media reporting using the term “payment fraud”;
- Reliance on alternative terminology such as “bank scam” or “online scam”;
- Lower levels of digital payment adoption or internet search activity.
The mid- and low-interest data suggest regional awareness gaps that could leave consumers and businesses more exposed. These areas represent opportunities for targeted education, regulatory engagement, and preventive measures, particularly as digital payments continue to expand.
REGIONAL SUMMURY
- Europe & UK: High awareness driven by strong regulation (FCA, PSD2) and active media reporting. Top indices in the UK and Ireland reflect proactive consumer protection and compliance focus.
- Asia-Pacific: Mixed pattern; Singapore and India show high engagement, while East and Southeast Asia remain lower, indicating uneven consumer education and fraud exposure.
- Africa: South Africa leads the region, reflecting high digital banking adoption and growing awareness of scams. Other African countries show limited search data, highlighting potential awareness gaps.
- North America: United States remains a consistent hotspot, with search activity reinforced by frequent data breach reporting and corporate fraud coverage.
Global awareness is strongest in digitally mature, English-speaking markets, while gaps persist in emerging or lower-penetration regions. These patterns can guide targeted fraud prevention, regulatory focus, and awareness campaigns.
Part Three: Regulatory Drivers and Major Events
Major regulatory changes in the UK over the past year have directly influenced global awareness of payment fraud, as reflected in Google Trends spikes. Legislative enforcement, rather than the volume of incidents, appears to be the primary driver of public and business attention.
KEY REGULATORY DEVELOPMENTS
- Mandatory Reimbursement for APP (Authorised Push Payment) Fraud (Oct 2024)
- PSPs participating in Faster Payments Scheme (FPS) or CHAPS must reimburse consumers, small businesses, and charities for losses from APP scams.
- Reimbursement capped at £85,000 per claim, with optional “claim excess” up to £100 (waived for vulnerable consumers).
- Aim: ensure most qualifying claims refunded within 5 working days.
- Payment Services (Amendment) Regulations 2024
- Amended the Payment Services Regulations 2017 to allow PSPs to delay outbound payments when fraud or dishonesty is suspected.
- Supports risk-based approaches to fraud prevention.
- FCA Safeguarding Rules for Payment & E-Money Firms (Aug 2025 announcement, May 2026 implementation)
- Requires ring-fencing of customer funds, daily checks, monthly reporting, and annual audits (smaller firms partially exempt).
- Goal: improve protection of customer funds and failure planning.
- “Failure to Prevent Fraud” Corporate Offence (Sept 2025)
- Introduces corporate criminal liability under the Economic Crime and Corporate Transparency Act 2023.
- Large organisations may be held responsible if reasonable procedures to prevent fraud are not in place.
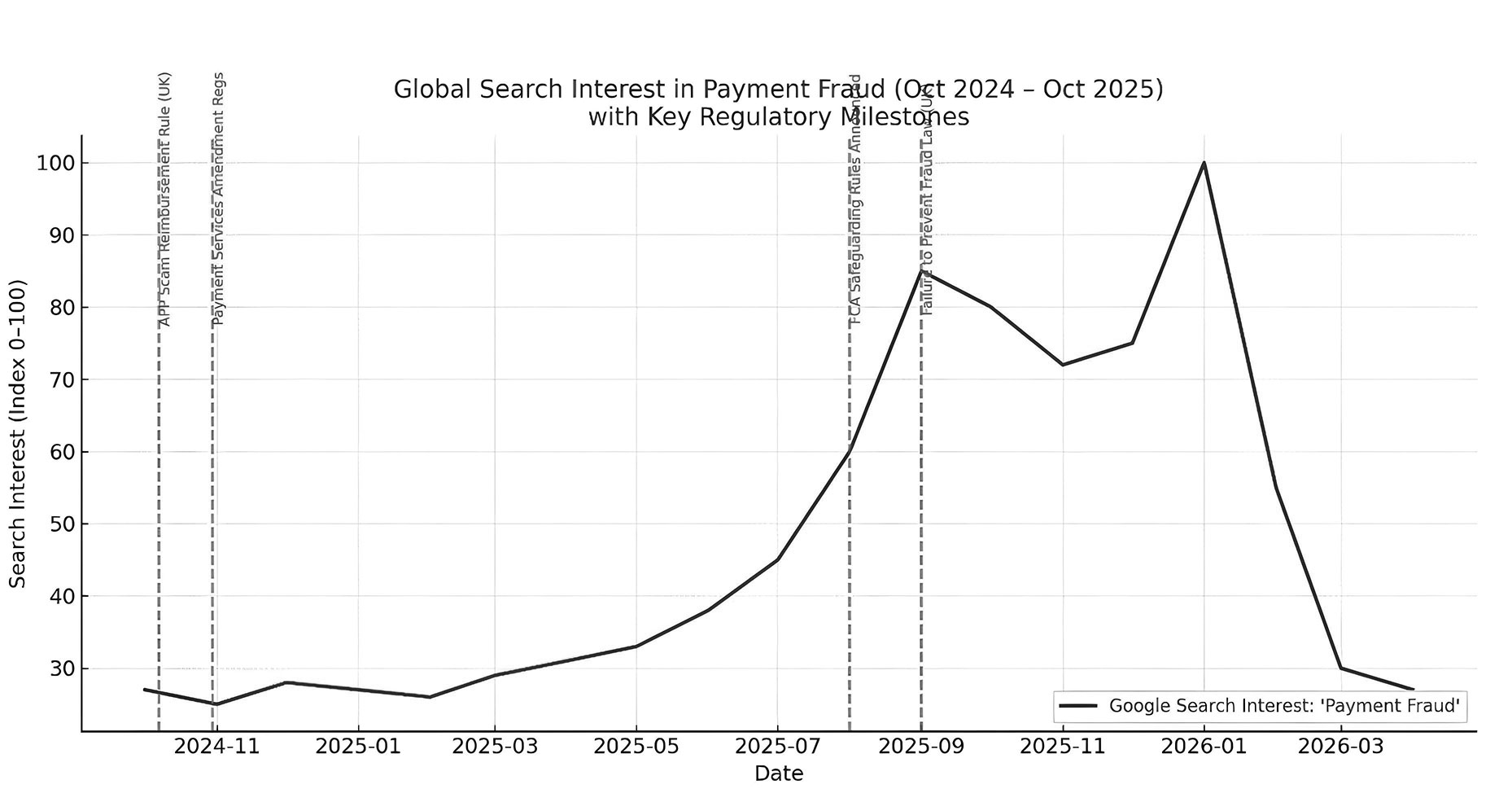
IMPACT ON GLOBAL AWARENESS
| Period | Event / Regulation | Observed Trend | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oct 2024 | APP Refund Regulation | Moderate rise (~27 → 33) | Public/media focus on reimbursement responsibility, especially in UK/ Commonwealth markets. |
| Late Oct 2024 | Payment Services Amendment | Steady growth | PSD2-style reforms renewed attention on digital payment compliance. |
| Sum 2025 | FCA Safeguarding Rules announced | Sharp rise (~85) | Increased liability and safeguarding reforms drove global search interest. |
| Sept 2025 | Failure to Prevent Fraud | Peak at 100 | Highest global attention; corporate fraud prevention dominated financial media. |
| After Sept 2025 | — | Return to baseline (~27) | Attention tapered as regulatory environment stabilised. |
Each major regulatory event correlated with a measurable increase in global search interest, demonstrating that policy and enforcement drive awareness more than crime volume. This underscores the importance of regulatory monitoring and proactive compliance for business leaders.
- UK & EU drove most search volume due to legislative activity.
- US interest increased in parallel, reflecting corporate discussion of UK fraud prevention frameworks.
- Asia-Pacific (Singapore, Australia) experienced secondary spikes as local markets adapted to similar safeguards.
The regulatory and enforcement landscape not only shapes public and business awareness but also reflects the evolving tactics of fraudsters. Understanding how fraud manifests - through phishing, business email compromise, synthetic identities, and digital payment exploitation - provides critical context for organisations to prioritise risk mitigation, strengthen controls, and target prevention efforts.
The next section examines the main payment fraud trends of 2024–2025, linking emerging techniques to observed awareness patterns and regional impacts.
Part Four: Main Payment Fraud Trends
In 2024–2025, payment fraud continued to evolve in both scale and sophistication. While traditional scams persist, fraudsters are increasingly exploiting digital channels, alternative payment methods, and emerging technologies. Understanding these trends is critical for businesses to anticipate threats, allocate resources, and strengthen prevention measures.
KEY FRAUD TYPES
1. Social Engineering and Impersonation Scams
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): Fraudsters spoof email accounts or use lookalike domains to trick organisations into making fraudulent payments.
- Phishing & Quishing: Emails and texts impersonate legitimate entities; quishing (QR code fraud) is rising, redirecting victims to malicious sites.
- Impersonation Scams: Criminals pose as family, friends, government agents, or company representatives to gain trust and access funds or information.
2. Account and Identity-Based Fraud
- Account Takeover (ATO): Surge of 76% in UK filings in early 2025, particularly in telecoms and online retail.
- Synthetic Identity Fraud: Combines real and fake information to create new identities for opening credit accounts.
- First-Party Misuse: Customers exploit return policies and refund processes for financial gain.
3. Exploitation of Digital and Alternative Payments
- Digital E-skimming (Magecart): Malicious code injected into e-commerce sites to steal payment data at checkout.
- Loyalty Point Fraud: Fraudsters target loyalty schemes, which often have weaker identity checks than traditional payments.
- Scam E-commerce: Fake online stores and listings trick consumers into paying for non-existent goods.
- Investment Scams: High-return promises, often involving fake cryptocurrencies or property schemes, continue to rise.
4. Other Notable Trends
- Cheque Fraud: Remains a frequent target, especially in corporate contexts despite the rise of digital payments.
- Use of Sophisticated Technology: AI-generated deepfakes and other advanced tools are increasingly used to create more realistic and effective scams.
It’s important to note that payment fraud is no longer confined to traditional channels. Digital payments, e-commerce platforms, loyalty schemes, and emerging technologies are key growth areas for criminal activity. Businesses must adapt by strengthening controls, monitoring emerging threats, and educating staff and customers to stay ahead of increasingly sophisticated fraud methods.
Part Five: Phishing, Crypto Scams and Global Enforcement
Fraud awareness is event-driven but geographically uneven. High search volumes correlate with digital adoption, regulatory coverage, and media reporting. Phishing and crypto scams are key emerging risks, especially where mobile payments and crypto usage are expanding rapidly. Enforcement has tangible impact, demonstrated by arrests, account freezes, and recovered funds, but prevention and education remain essential, particularly in mid- and low-awareness regions.
Phishing and cryptocurrency-related scams are increasingly prominent in the payment fraud landscape. Google Trends data shows where awareness is rising, while global enforcement actions reveal where authorities are actively intervening. Understanding both helps businesses anticipate risk, prioritise prevention, and align with regulatory expectations.
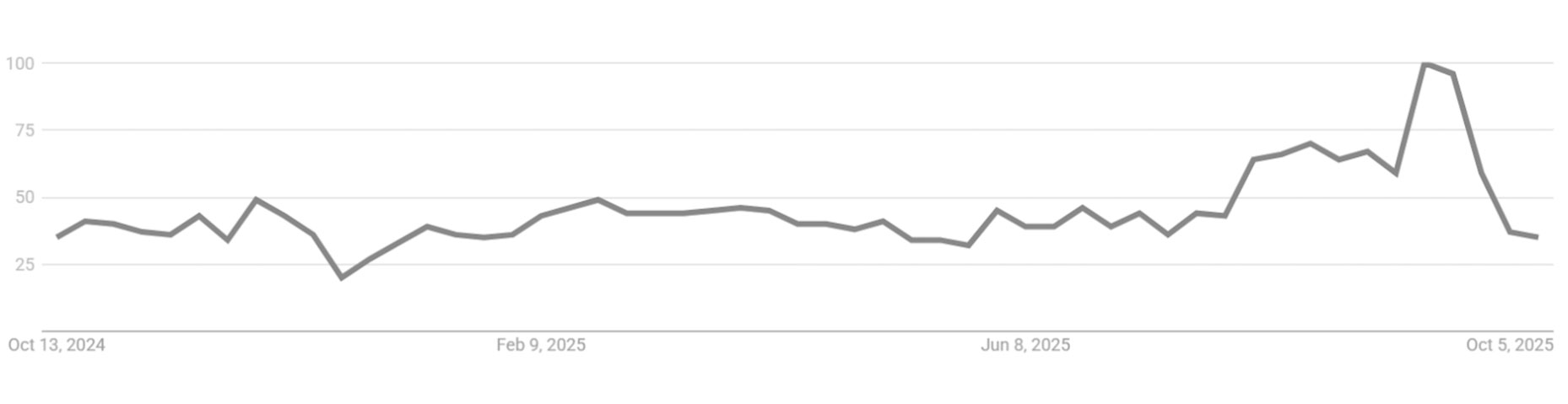
PHISHING SCAMS – GLOBAL AWARENESS
Phishing remains a primary social engineering tactic, with quishing (QR code fraud) emerging as a notable risk. High search interest correlates with digital adoption, regulatory awareness, and media coverage, showing which markets are most alert.
Top countries by search interest (Oct 2024–Oct 2025):
| Country | Index |
|---|---|
| St. Helena | 100 |
| Singapore | 78 |
| Philippines | 57 |
| Australia | 50 |
| United States | 35 |
| New Zealand | 35 |
| Canada | 28 |
| United Kingdom | 28 |
| Kenya | 21 |
| Malaysia | 21 |
PHISHING SCAMS WORLDWIDE – INTEREST OVER TIME
CRYPTO SCAMS – GLOBAL AWARENESS
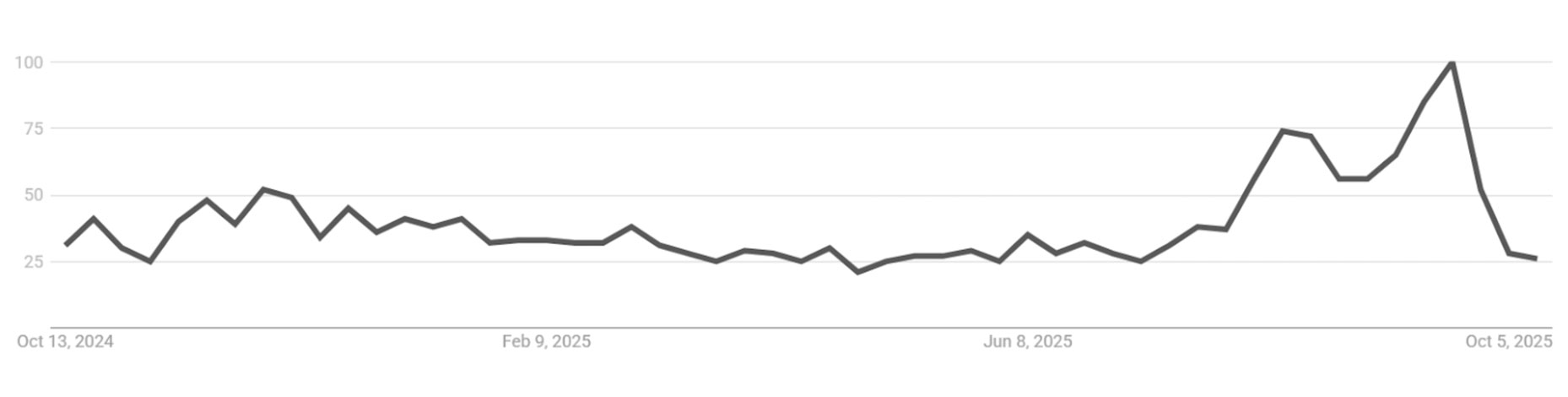
Crypto scams often involve fraudulent investment schemes, including fake cryptocurrencies and property scams. Rising awareness in emerging markets reflects growing crypto adoption and exposure to online scams, while low interest in parts of Europe and East Asia may indicate either lower engagement or use of alternative terminology.
Top countries by search interest (Oct 2024–Oct 2025):
| Country | Index |
|---|---|
| St. Helena | 100 |
| Nigeria | 57 |
| Cambodia | 50 |
| Singapore | 50 |
| Australia | 35 |
| Canada | 35 |
| Kenya | 35 |
| United States | 28 |
| United Kingdom | 28 |
| South Africa | 21 |
CRYPTO SCAMS WORLDWIDE TRENDS – OVER TIME
GLOBAL ENFORCEMENT OPERATIONS
While a single global arrest count for payment fraud in 2024-2025 is not available, operations like Interpol's and Operation First Light have led to thousands of arrests.
| Operation | Period | Scope | Key Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| INTERPOL HAECHI VI | Apr–Aug 2025 | 40 countries; cyber-enabled financial crimes | 68,000 bank accounts disrupted; ~400 crypto wallets frozen; USD 439M recovered |
| Operation First Light | 2024 | Multi-continent online scams | 3,950 arrests; 14,643 potential suspects; USD 257M in assets seized |
| UK Finance's Banking Protocol | 2024 | Corporate fraud prevention | 136 arrests; £61.3M losses prevented |
- UK & EU: Legislative and regulatory frameworks drove search volume and enforcement coordination.
- US: Interest rose in parallel, reflecting corporate adoption of UK-style fraud prevention practices.
- India: Reports mention ongoing arrests related to digital scams, highlighting a significant crackdown on a type of online scam that targets Indian citizens.
- Hong Kong: Multiple suspects were arrested as part of the global effort to combat phishing, investment fraud, and other scams.
The combined insights from global search trends, regional awareness, regulatory developments, and enforcement actions reveal a clear picture: payment fraud is increasingly sophisticated, digitally enabled, and geographically varied. While major regulatory announcements and enforcement operations drive temporary spikes in attention, underlying risk continues to grow across both mature and emerging markets.
Conclusion and Outlook
The 2024–2025 period demonstrates that payment fraud is dynamic, complex, and increasingly global. While public and business attention tends to spike around regulatory announcements and high-profile incidents, baseline awareness is gradually rising, particularly in digitally mature markets. Fraudsters are leveraging social engineering, digital payments, e-commerce, and emerging technologies like AI to exploit both individuals and organisations.
Regional patterns highlight where vigilance is strongest and where gaps persist. Mature markets with robust regulation and media coverage show higher awareness, while emerging and lower-penetration markets display uneven engagement, emphasising the need for targeted education and preventive measures. Regulatory developments, especially those enhancing corporate responsibility and safeguarding consumer funds, have proven effective at increasing attention and shaping behaviors, while enforcement operations demonstrate that coordinated global action can disrupt criminal networks and recover significant assets.
Looking ahead to 2025–2026, several trends are likely to shape the fraud landscape. Social engineering and identity-based fraud will continue to evolve, particularly in digital and alternative payment channels. AI-enabled scams and sophisticated technology-driven attacks are expected to increase in frequency and sophistication. Businesses that proactively monitor emerging threats, strengthen fraud detection and prevention measures, and align with regulatory and compliance requirements will be best positioned to reduce exposure and protect stakeholders.
In short, payment fraud will remain a moving target, but by leveraging awareness, data-driven insights, and adaptive risk management, businesses can stay ahead of evolving threats and mitigate both financial and reputational impact.